Embark on a musical odyssey with the C# half diminished 7th chord, a harmonious entity that tantalizes the ears with its intriguing structure and versatile functionality. This enigmatic chord, a cornerstone of music theory and composition, beckons us to delve into its sonic intricacies and explore its practical applications for musicians of all stripes.
Crafted from a blend of minor 3rd, augmented 5th, and diminished 7th intervals, the C# half diminished 7th chord exudes a distinctive aura of tension and release. Its unique sound has captivated musicians for centuries, inspiring countless melodies and harmonic progressions.
Understanding the C# Half Diminished 7th Chord
The C# half diminished 7th chord is a versatile jazz chord that adds a sophisticated and dissonant flavor to music. Understanding its structure and intervals is essential for guitarists and musicians.
Structure and Intervals
The C# half diminished 7th chord is composed of four notes: the root (C#), the minor third (E), the augmented fifth (G#), and the diminished seventh (B).
The intervals between the notes are:
- Root to minor third: minor third (3 semitones)
- Minor third to augmented fifth: augmented second (3 semitones)
- Augmented fifth to diminished seventh: minor third (3 semitones)
Chord Voicings and Inversions
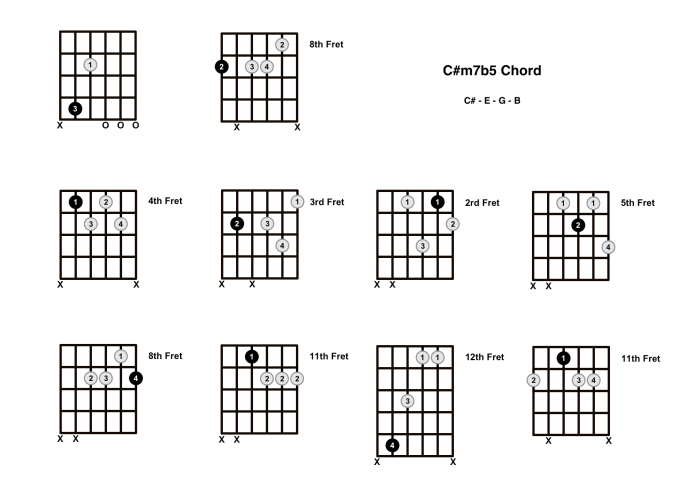
The C# half diminished 7th chord can be voiced in various ways, each producing a unique sound and harmonic effect. Inversions refer to the arrangement of the chord’s notes, with the root note appearing in different positions within the chord.
Chord Voicings
| Position | Voicing |
|---|---|
| Root Position | C#
|
| 1st Inversion | E
|
| 2nd Inversion | G
|
| 3rd Inversion | B
|
Each voicing emphasizes different intervals within the chord, creating distinct harmonic qualities.
Inversions, C# half diminished 7th chord
Inversions impact the chord’s sound and functionality. The root position emphasizes the fundamental relationship between the root and the other notes. As the chord is inverted, the bass note changes, altering the intervallic relationships and creating different harmonic tensions and resolutions.
For example, the 1st inversion (E – G – B – C#) highlights the tritone interval between E and B, creating a more dissonant and unstable sound. In contrast, the 3rd inversion (B – C# – E – G) emphasizes the perfect fourth interval between B and E, resulting in a more consonant and stable sound.
Harmonic Function and Context
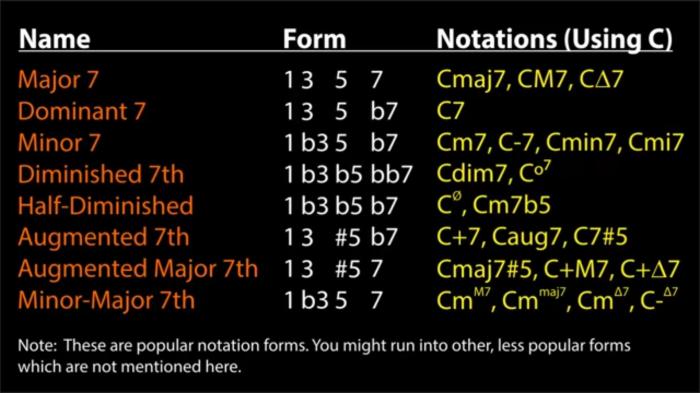
The C# half diminished 7th chord, often abbreviated as C#ø7, serves various harmonic functions in musical contexts.
Firstly, C#ø7 can function as a pre-dominantchord, leading to the dominant chord (G#7) and ultimately resolving to the tonic (C# major). This is a common progression in tonal music.
C#ø7 is also frequently used as a substitutefor other chords. It can effectively replace the V7 chord (G#7) in certain situations, particularly when a stronger sense of dissonance is desired.
Additionally, C#ø7 can be used as a substitutefor the ii7b5 chord (D#ø7). This substitution adds a chromatic element to the progression and can create a more complex and sophisticated sound.
The C# half diminished 7th chord, with its complex yet alluring sound, is a staple in jazz and other genres. Its intricate interplay of notes creates a unique tension that resolves beautifully. Speaking of complex interactions, have you ever wondered about the chemical reaction between pbcl2 agno3 pb no3 2 agcl? Here’s an insightful exploration that delves into the fascinating world of chemistry.
Returning to our musical realm, the C# half diminished 7th chord continues to captivate listeners with its expressive and versatile nature.
Applications in Music Theory and Composition: C# Half Diminished 7th Chord
The C# half diminished 7th chord finds versatile applications in music theory and composition, offering unique harmonic possibilities.
- Chord Progressions:The C# half diminished 7th chord can create interesting chord progressions by resolving to various other chords. For instance, it commonly resolves to the dominant 7th chord (G#7) or the minor 7th chord (E7).
- Harmonic Analysis:In harmonic analysis, the C# half diminished 7th chord is often used as a secondary dominant chord.
It serves as a temporary tonicization of another key, providing harmonic tension before resolving back to the original key.
- Tension and Resolution:The C# half diminished 7th chord creates a sense of tension due to its dissonant intervals. When resolved to a consonant chord, such as a major or minor triad, it creates a satisfying sense of resolution.
Practical Applications for Musicians

The C# half diminished 7th chord offers a rich and versatile sound that can enhance both guitar and piano playing. Here are some practical tips for incorporating this chord into your music:
For Guitarists
To play the C# half diminished 7th chord on the guitar, use the following fingering: 1st fret on the 1st string, 2nd fret on the 2nd string, 3rd fret on the 3rd string, and 4th fret on the 4th string.
This chord can be used in various contexts, such as jazz, blues, and rock. Try experimenting with different strumming patterns and voicings to create unique sounds.
For Pianists
On the piano, the C# half diminished 7th chord is played as follows: C# (root), E (minor 3rd), G (perfect 5th), and Bb (diminished 7th).
This chord adds a sophisticated touch to piano compositions. Experiment with different voicings and inversions to explore its harmonic possibilities.
Essential FAQs
What is the structure of the C# half diminished 7th chord?
C# Half Diminished 7th consists of C#, E, G#, and B.
How is the C# half diminished 7th chord commonly notated?
It can be notated as C#dim7, C#ø7, or C#m7b5.
What is the harmonic function of the C# half diminished 7th chord?
It often functions as a substitute for the V7 chord, adding tension and leading to resolution.