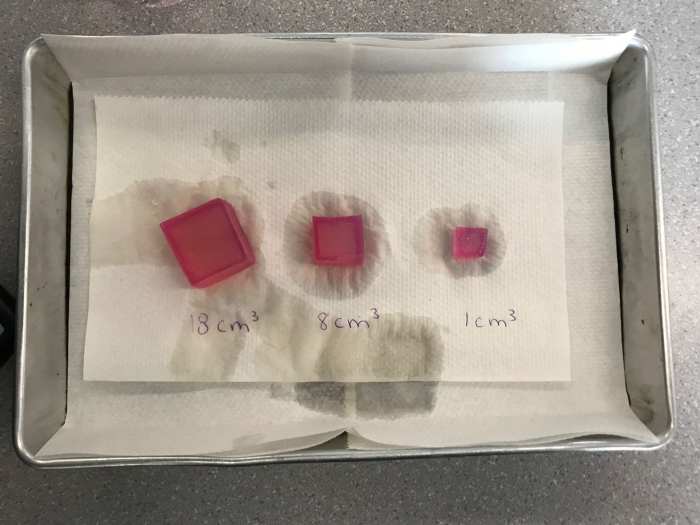
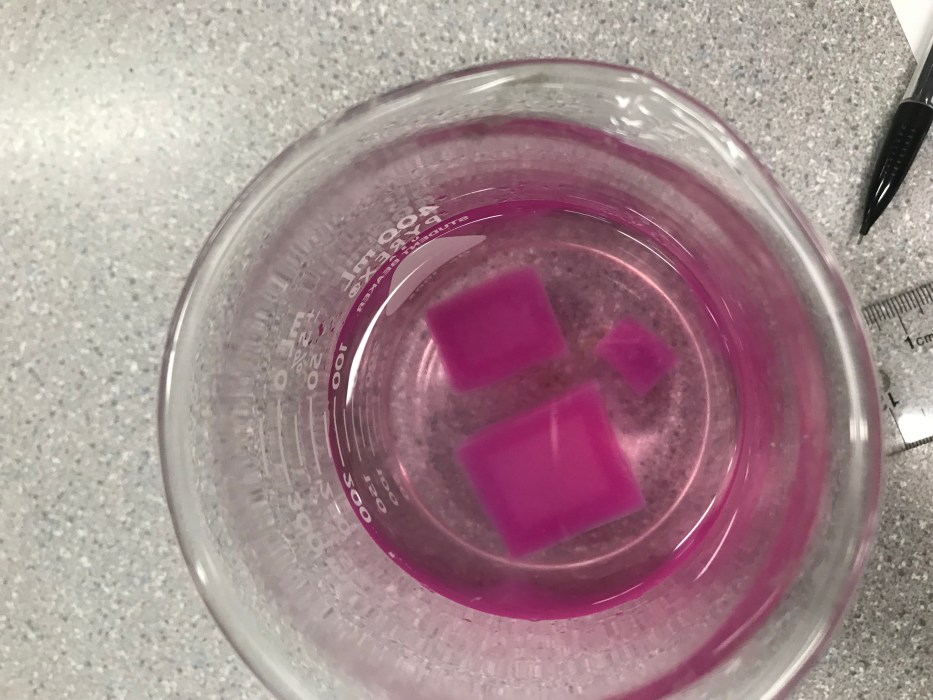
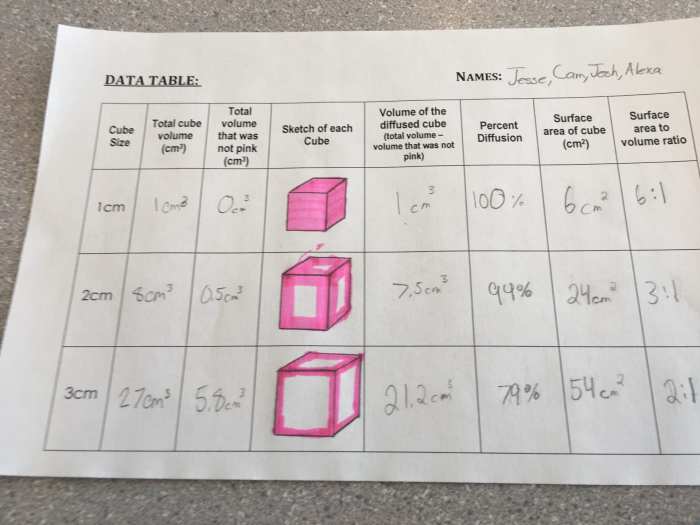
Diffusion in agar cubes lab answer key takes center stage, offering a comprehensive guide to the intricate processes of diffusion in agar cubes. This exploration delves into the concept, experimental design, data analysis, and factors influencing diffusion, providing a solid foundation for understanding this crucial scientific technique.
Agar cubes, meticulously prepared to ensure standardized dimensions, serve as a controlled environment for studying diffusion. Through carefully designed experiments, researchers can precisely measure the diffusion coefficient, a key parameter that quantifies the rate of solute movement within the agar matrix.
Diffusion in Agar Cubes
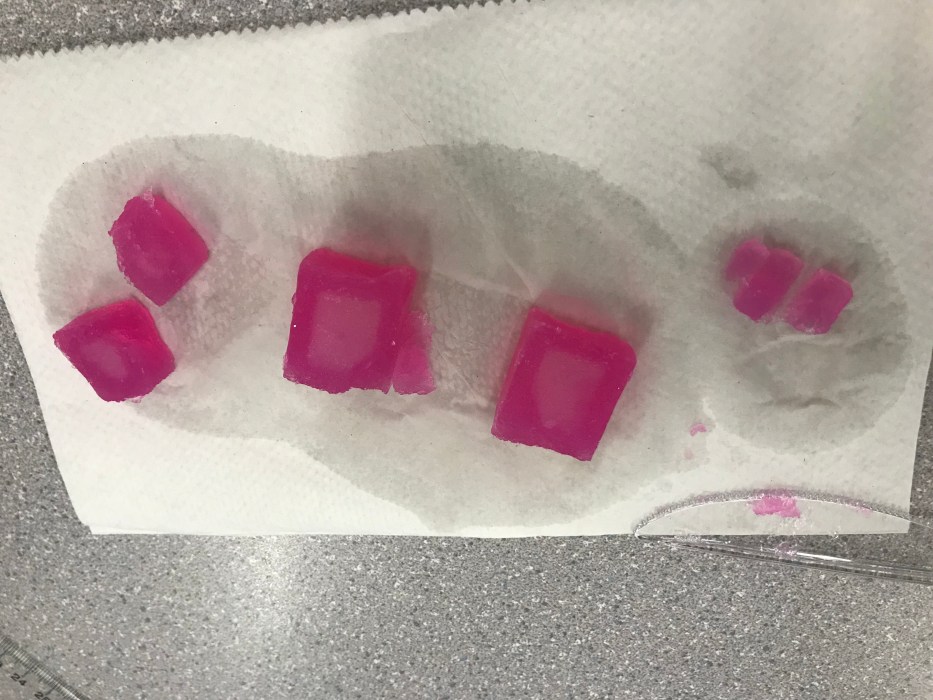
Diffusion is a fundamental process that describes the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This process occurs in many biological and chemical systems, including the diffusion of solutes in agar cubes.
In agar cubes, diffusion occurs when a solute is placed in contact with the cube. The solute molecules then diffuse into the cube, spreading out until they reach a uniform concentration throughout the cube. The rate of diffusion is determined by several factors, including the concentration of the solute, the size of the cube, and the temperature.
Agar Cube Preparation
Agar cubes are typically made from a mixture of agar powder and water. The agar powder is dissolved in water and then heated until it boils. The boiling mixture is then poured into a mold and allowed to cool and solidify.
The resulting agar cubes are then ready to be used for diffusion experiments.
It is important to standardize the size and shape of the agar cubes when preparing them. This ensures that the diffusion process is consistent from one cube to the next.
Experimental Design
To design an experiment to measure diffusion in agar cubes, the following steps should be followed:
- Select a solute to be used in the experiment.
- Prepare a series of agar cubes of known size and shape.
- Place the solute in contact with the agar cubes.
- Measure the concentration of the solute in the agar cubes over time.
- Plot the concentration data against time to determine the diffusion coefficient.
The diffusion coefficient is a measure of the rate of diffusion. It is calculated using the following equation:
D = (x^2) / (2t)
where:
- D is the diffusion coefficient (cm^2/s)
- x is the distance traveled by the solute (cm)
- t is the time (s)
Data Collection and Analysis
Data on the diffusion of solutes in agar cubes can be collected using a variety of methods. One common method is to use a spectrophotometer to measure the absorbance of the solute at different depths in the agar cube. The absorbance data can then be used to calculate the concentration of the solute at each depth.
Once the concentration data has been collected, it can be analyzed to determine the diffusion coefficient. The diffusion coefficient can be calculated using the equation provided above.
Factors Affecting Diffusion, Diffusion in agar cubes lab answer key
The rate of diffusion in agar cubes is affected by several factors, including:
- Concentration of the solute
- Size of the agar cube
- Temperature
- pH
- Presence of other solutes
The concentration of the solute has a direct effect on the rate of diffusion. The higher the concentration of the solute, the faster the rate of diffusion. This is because there are more solute molecules available to diffuse.
The size of the agar cube also affects the rate of diffusion. The larger the agar cube, the slower the rate of diffusion. This is because the solute molecules have to travel a longer distance to reach the center of the cube.
Temperature also affects the rate of diffusion. The higher the temperature, the faster the rate of diffusion. This is because the solute molecules have more energy at higher temperatures.
pH can also affect the rate of diffusion. The pH of the agar cube can affect the solubility of the solute. If the solute is more soluble at a particular pH, then the rate of diffusion will be faster.
The presence of other solutes can also affect the rate of diffusion. If the agar cube contains other solutes, then the solute molecules will have to compete with the other solutes for space. This can slow down the rate of diffusion.
Applications of Diffusion in Agar Cubes
Diffusion in agar cubes has a number of applications in scientific research. One application is the study of drug absorption. By measuring the rate of diffusion of a drug in an agar cube, researchers can determine how quickly the drug will be absorbed into the body.
Another application of diffusion in agar cubes is the study of membrane permeability. By measuring the rate of diffusion of a solute across an agar cube membrane, researchers can determine the permeability of the membrane to that solute.
Question & Answer Hub: Diffusion In Agar Cubes Lab Answer Key
What is the purpose of using agar cubes in diffusion experiments?
Agar cubes provide a standardized and controlled environment for studying diffusion, allowing researchers to accurately measure diffusion coefficients and investigate the factors affecting solute movement.
How is the diffusion coefficient calculated in agar cube experiments?
The diffusion coefficient is calculated by analyzing the concentration gradient of the solute over time and applying Fick’s second law of diffusion.
What are some factors that can affect the rate of diffusion in agar cubes?
Factors such as temperature, solute concentration, agar concentration, and the presence of obstacles can influence the rate of diffusion in agar cubes.