The combustion of ethane produces carbon dioxide and steam – The combustion of ethane, a hydrocarbon commonly found in natural gas, produces carbon dioxide and steam. This process plays a significant role in various industrial and domestic applications, but it also has environmental implications that warrant attention. Understanding the chemical equation, products, reaction conditions, and applications of ethane combustion is crucial for harnessing its benefits while mitigating its potential drawbacks.
The combustion of ethane, represented by the balanced chemical equation C2H6 + 7O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O, involves the complete oxidation of ethane in the presence of oxygen. The stoichiometry of the reaction dictates the precise proportions of reactants required for complete combustion.
Combustion of Ethane: The Combustion Of Ethane Produces Carbon Dioxide And Steam

The combustion of ethane is a chemical reaction that produces carbon dioxide and steam. This reaction is used to generate energy in various industrial and domestic applications.
Chemical Equation, The combustion of ethane produces carbon dioxide and steam
The balanced chemical equation for the combustion of ethane is as follows:
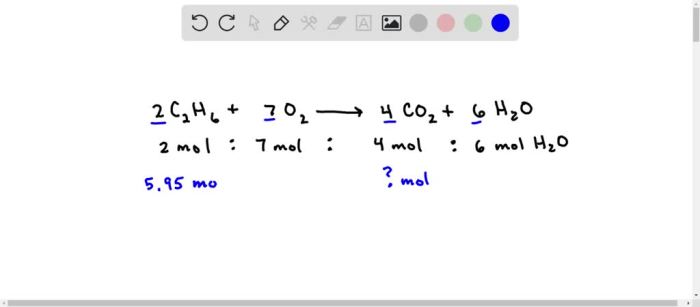
C2H 6+ 7O 2→ 4CO 2+ 6H 2O
This equation indicates that two molecules of ethane react with seven molecules of oxygen to produce four molecules of carbon dioxide and six molecules of water.
Products of Combustion
- Carbon Dioxide:Carbon dioxide is a colorless, odorless gas that is heavier than air. It is a greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming.
- Steam:Steam is a colorless, odorless gas that is lighter than air. It is a major component of the atmosphere and is essential for life on Earth.
Reaction Conditions
The combustion of ethane occurs optimally under the following conditions:
- Temperature:The ideal temperature for the combustion of ethane is between 800 and 1200 degrees Celsius.
- Pressure:The combustion of ethane is not significantly affected by pressure.
- Catalyst:A catalyst, such as platinum or palladium, can be used to increase the rate of the combustion reaction.
Applications
The combustion of ethane has numerous industrial and domestic applications, including:
- Power Generation:Ethane is used as a fuel to generate electricity in power plants.
- Heating:Ethane is used as a fuel for heating homes and businesses.
- Transportation:Ethane is used as a fuel for vehicles, such as buses and trucks.
Environmental Impact
The combustion of ethane releases greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, into the atmosphere. These gases contribute to global warming and climate change.
Additionally, the combustion of ethane can produce air pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides and particulate matter. These pollutants can cause respiratory problems and other health issues.
Energy Considerations
The combustion of ethane releases a significant amount of energy. The energy content of ethane is approximately 46.3 megajoules per kilogram.
This energy is utilized in various applications, such as power generation, heating, and transportation.
Safety Considerations
The combustion of ethane can pose safety hazards, including the risk of explosions and fires.
Proper precautions should be taken to prevent accidents, such as using proper ventilation, avoiding ignition sources, and storing ethane safely.
FAQ Section
What are the physical properties of carbon dioxide produced from ethane combustion?
Carbon dioxide is a colorless, odorless, and non-flammable gas at room temperature and pressure. It is heavier than air and has a density of approximately 1.98 kg/m3.
How does the presence of a catalyst affect the combustion of ethane?
Catalysts, such as platinum or palladium, can significantly lower the activation energy required for ethane combustion, thereby increasing the reaction rate and completeness of the process.