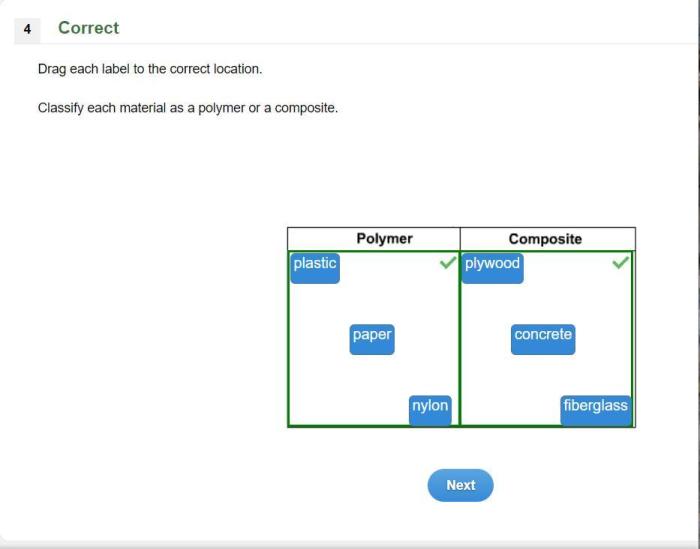
Classify each material as a polymer or a composite – this task requires a deep understanding of the fundamental differences between these two classes of materials. Polymers, composed of long chains of repeating units, exhibit unique properties such as flexibility, strength, and electrical insulation.
Composites, on the other hand, are hybrid materials combining two or more distinct phases to achieve enhanced properties not found in the individual components.
This comprehensive guide delves into the realm of polymers and composites, exploring their distinct characteristics, applications, and the factors that govern their suitability for various engineering challenges.
Polymer vs. Composite: Definition and Properties: Classify Each Material As A Polymer Or A Composite
In materials science, polymers and composites are two distinct material classes with unique properties and applications.
Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units called monomers. Polymers exhibit a wide range of properties, including flexibility, elasticity, and thermal insulation.
Composite
A composite is a material made from two or more distinct materials with significantly different properties. The resulting material combines the properties of the individual components, creating a material with enhanced performance.
Key Differences
- Polymers are composed of a single type of repeating unit, while composites consist of multiple materials.
- Polymers are typically flexible and lightweight, while composites can be engineered to have a wide range of properties.
- Composites are generally stronger and more durable than polymers due to the combination of different materials.
Types of Polymers

Polymers are classified into different types based on their chemical structure and properties.
- Thermoplastics: These polymers can be melted and reshaped repeatedly without losing their properties.
- Thermosets: These polymers undergo a chemical change upon heating, becoming rigid and permanently set.
- Elastomers: These polymers exhibit rubber-like properties, including high elasticity and flexibility.
- Biopolymers: These polymers are produced by living organisms and are biodegradable.
| Type | Structure | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastic | Linear or branched chains | Flexible, recyclable, low strength |
| Thermoset | Cross-linked chains | Rigid, strong, heat-resistant |
| Elastomer | Amorphous or semi-crystalline | Elastic, flexible, low strength |
| Biopolymer | Natural or synthetic | Biodegradable, renewable, often weaker |
Types of Composites
Composites are classified based on their composition and structure.
- Matrix Composites: These composites consist of a continuous matrix material reinforced with fibers or particles.
- Laminated Composites: These composites are made by layering different materials together, such as fiberglass or carbon fiber.
- Hybrid Composites: These composites combine different types of reinforcements, such as fibers and particles, in a single matrix.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Composites
Advantages
- High strength and stiffness
- Lightweight
- Corrosion resistance
- Design flexibility
Disadvantages
- Higher cost than traditional materials
- Complex manufacturing processes
- Susceptibility to damage
Applications of Polymers and Composites
Polymers
- Plastic packaging
- Automotive parts
- Medical devices
- Construction materials
- Textiles
Composites
- Aerospace structures
- Automotive parts
- Sporting goods
- Wind turbine blades
- Medical implants
Comparison of Polymers and Composites
- Strengths
- Polymers: Flexibility, low cost, lightweight
- Composites: High strength, stiffness, lightweight
- Weaknesses
- Polymers: Lower strength, susceptibility to heat
- Composites: Higher cost, complex manufacturing
- Suitability for Applications
- Polymers: Ideal for applications requiring flexibility, low cost, and low weight
- Composites: Suitable for applications demanding high strength, stiffness, and lightweight, even in harsh environments
Expert Answers
What is the primary distinction between a polymer and a composite?
Polymers are composed of long, repeating molecular chains, while composites are hybrid materials that combine two or more distinct phases.
What are the key properties of polymers?
Polymers are typically flexible, strong, and possess excellent electrical insulation properties.
What are the advantages of using composites?
Composites offer enhanced strength, stiffness, and thermal stability compared to their individual components.
