Earth science the physical setting answers – Embark on a journey of discovery with Earth Science: The Physical Setting Answers, a comprehensive exploration of our planet’s intricate systems and dynamic processes. This captivating guide unveils the secrets of Earth’s history, structure, atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, climate, resources, and more, providing a profound understanding of the physical setting that sustains life.
Through engaging narratives and authoritative insights, this resource delves into the fundamental concepts that shape our planet, empowering readers with a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems and the challenges and opportunities they present.
Earth’s Systems
Earth’s systems are interconnected and interdependent, constantly interacting to maintain the planet’s delicate balance. These systems include the geosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere.
The geosphere comprises Earth’s solid components, including the crust, mantle, and core. The hydrosphere encompasses all water bodies, both surface and subsurface. The atmosphere is the gaseous envelope surrounding Earth, providing essential gases for life and regulating temperature. Finally, the biosphere consists of all living organisms and their interactions with the environment.
Interactions between Earth’s Systems, Earth science the physical setting answers
- The geosphere provides minerals and nutrients for the hydrosphere and biosphere.
- The hydrosphere shapes the geosphere through erosion and deposition, and provides water for the atmosphere and biosphere.
- The atmosphere regulates Earth’s temperature, protects it from harmful radiation, and provides oxygen for the biosphere.
- The biosphere influences the geosphere through the formation of soils and the release of gases into the atmosphere.
These interactions demonstrate the intricate interconnectedness of Earth’s systems, emphasizing the need for a holistic approach to understanding and managing our planet.
Earth’s History: Earth Science The Physical Setting Answers
The geologic time scale provides a framework for understanding Earth’s vast history. It divides time into eons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages, each representing significant geological events and changes.
Major Events in Earth’s History
- Formation of Earth:Approximately 4.54 billion years ago, Earth formed from the accretion of cosmic dust and gas.
- Evolution of Life:The first evidence of life appeared about 3.5 billion years ago, evolving from simple organisms to complex life forms.
- Ice Ages:Earth has experienced multiple ice ages throughout its history, with the most recent ending about 11,700 years ago.
These events have shaped Earth’s landscape, climate, and ecosystems, providing insights into the planet’s dynamic history.
Earth’s Structure

Earth’s internal structure is layered, with each layer exhibiting distinct characteristics and compositions.
Internal Structure
- Crust:The outermost layer, composed of solid rock, ranging from 5 to 70 kilometers thick.
- Mantle:A thick layer of solid rock beneath the crust, extending to a depth of about 2,900 kilometers.
- Core:The innermost layer, consisting of an outer liquid layer and an inner solid layer, with a radius of about 1,220 kilometers.
The composition and properties of these layers vary significantly, influencing Earth’s processes and phenomena.
Earth’s Atmosphere
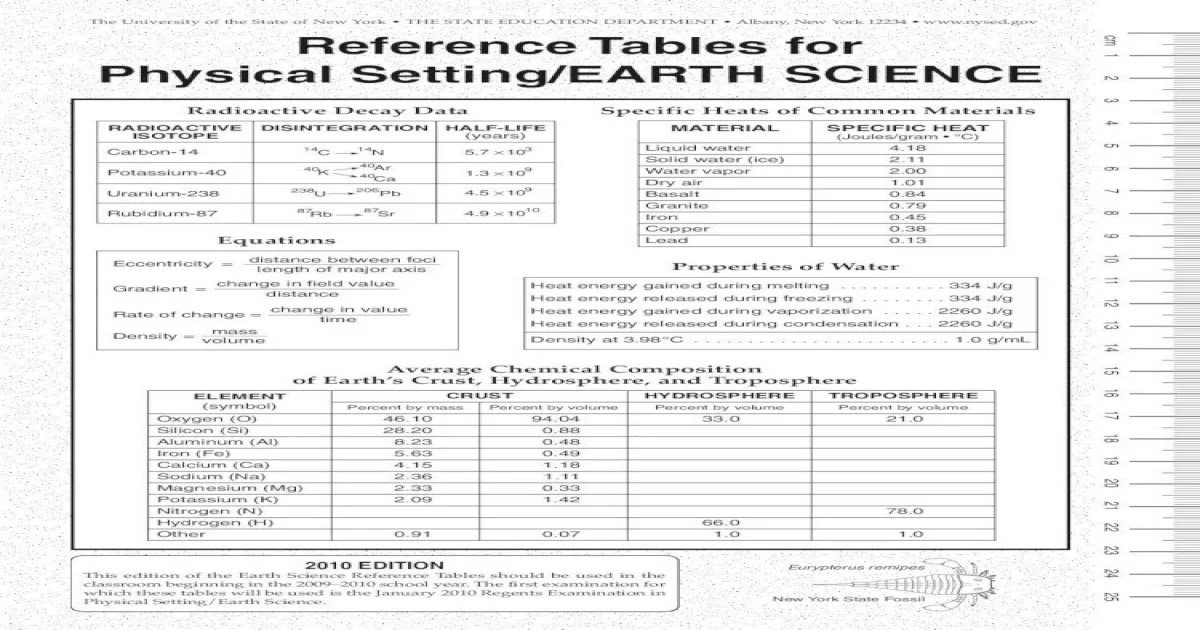
Earth’s atmosphere is a dynamic gaseous envelope surrounding the planet. It plays a crucial role in regulating temperature, protecting from harmful radiation, and providing essential gases for life.
Composition and Structure
- Nitrogen:Comprises about 78% of the atmosphere.
- Oxygen:Essential for life, constituting about 21% of the atmosphere.
- Other gases:Include argon, carbon dioxide, and trace amounts of other gases.
The atmosphere is divided into layers based on temperature and composition, including the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere.
Common Queries
What is the geologic time scale?
The geologic time scale is a system of chronological divisions that represents the history of Earth. It is divided into eons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages, and provides a framework for understanding the sequence of geologic events and the evolution of life on Earth.
What are the four Earth systems?
The four Earth systems are the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, and biosphere. The atmosphere is the layer of gases surrounding the Earth, the hydrosphere is the water on and below the Earth’s surface, the geosphere is the solid Earth, and the biosphere is the living organisms on Earth.
What is the greenhouse effect?
The greenhouse effect is the process by which thermal radiation from a planetary surface is absorbed by atmospheric greenhouse gases, and is re-radiated in all directions. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect on Earth.